AI Methods and Practices
AI Opportunity Analysis
Discovering and selecting impactful Artificial Intelligence Applications can be elusive as there are no defined practices that enable business professionals and technology executives to disambiguate the predictive capacity among potential candidates. During its initial entry into AI, SmartSystems was frequently confronted with this challenge, and after several years of AI modeling and deployment the selection heuristics were analyzed and classified, revealing four formal techniques which we now apply when scouting for AI application candidates. These techniques are: 1) Data Exploration, 2) Decision Science, 3) Domain Ontology, and 4) Knowledge Engineering, and are collectively called the SmartSystems AI Opportunity Analysis Framework.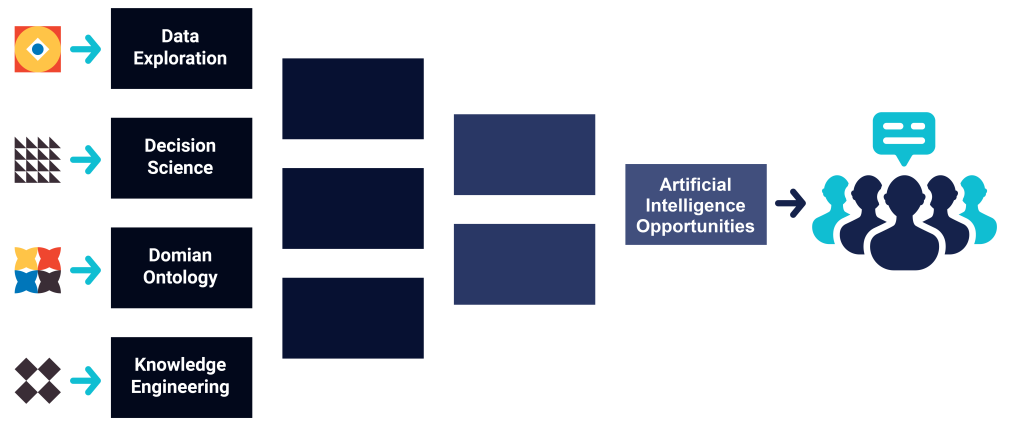
Data Exploration
Exploratory data analysis (EDA) is a process of analyzing and visualizing data in order to understand its characteristics, patterns, and relationships. This practice enables SmartSystems to uncover hidden data characteristics that are invisible to the unaided observer. It involves examining the data from multiple angles, using a variety of techniques to uncover insights and identify potential trends or patterns. EDA is typically the first step in a Data Analysis or Machine Learning project and is a flexible and iterative process that allows our Data Scientists to explore the data freely and follow their curiosity, rather than being constrained by a predetermined set of hypotheses or models.
The goal of our Data Exploration practice is to gain a deeper understanding of the data and to generate prediction ideas for further analysis or hypothesis testing. It is an important part of our AI Identification and Selection Process, as it helps to unravel potential classification and predictive characteristics with the data or with the assumptions underlying how the data is used. This help to guide the development of more sophisticated AI and Machine Learning Models that can positively impact business functions and operational processes. We then transform these newly discovered data science applications and machine learning models into AI implementations that facilitate targeted business domains.
Data Exploration is the first line of defense embraced by Data Scientists, AI Engineers, and Machine Learning Practitioners when contemplating AI applications. The approach is widely applied in SmartSystems engagements and among our clientele. In fact, the global market for data visualization and analysis was valued at $12.4 billion in 2020 and expected to reach $28.8 billion by 2025, growing at a compounded rate of 19.2% to 2025. Other research suggests that most businesses considering AI choose EDA as the most cost effective vehicle to pinpoint pragmatic implementations. SmartSystems also executes EDA as independent consulting engagements, as this market is flourishing and anticipated to reach of $40 billion by 2030.
Decision Science
As a computing trailblazer, SmartSystems has implemented numerous applications that enforce operations research and optimization algorithms, indirectly developing a deep passion for Decision Science along the way. For over a decade we have been applying Decision Science techniques to help businesses make better decisions through the guidance of scientific and mathematical principles. This drives informed and rational decisions by providing a systematic framework for considering and comparing different options. The heuristics we accumulate in applying decision science techniques in dealing with complex business choices unravels observations on how prediction can be effectively applied to be preemptive.
SmartSystems applies Decision Science to help organizations identify and evaluate the trade-offs involved in different courses of action, highlighting those options that are most likely to achieve their goals. By applying these approaches, SmartSystems is able to glean how machine learning algorithms can be infused into decision making workflows to decompress the clutter at critical decision chokepoints in business operations. Observations and discoveries on how decision chokepoints can be AI enabled can be reinforced through the accumulated history of the successes and failures of past decisions. This retrospective can be further capitalized by the ML algorithms to preempt future choices leading to greater predictive accuracy.
Decision science is used in a wide range of industries including finance, marketing, healthcare, and public policy. It involves tools and techniques from a variety of disciplines, including economics, psychology, statistics, and computer science to understand complex decision making. SmartSystems utilizes numerous decision science techniques and processes to inform effective decision making and to seek approaches that can be AI codified. Since these techniques are interdisciplinary, it is difficult to quantify its market size and growth. However, including operations research and optimization, the market size suggests a value of $5.6 billion in 2020 and $13.5 billion in 2025, with the potential to exceed $20 billion by 2030.
Domain Ontology
Assimilation of an Ontology inevitably translates into a comprehensive understanding of the business domain or subject matter being deconstructed and resynthesized. SmartSystems has acquired this skill through the years of experience it has attained modeling large scale information repositories on specific domains such as energy, manufacturing, and supply chain. The ontology we create represents the concepts, entities, and relationships that are relevant to a particular domain, and provides a common language and framework for understanding, analyzing, and responding to situations and events within that domain. This structured body of domain specific information reveals valuable business nuances exploitable by AI.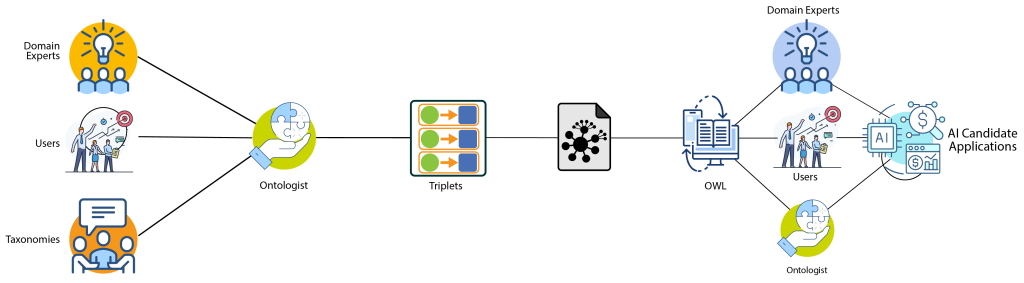
We typically express an ontology employing a formal language called OWL (Web Ontology Language), which allows the model to be semantically understood and easily processed using close to natural language dialog. In fact, an ontology assimilated using OWL readily lends itself to be interrogated by non computing professionals. This level of openness results in wider use of the ontology as the underlining complexities of the model are insulated from the user, encouraging further use and the possibility of unraveling relationships that are capturable by ML algorithms. An ontology can be used to represent any of a wide range of domains, including business, science, and healthcare; and is one of our key instruments to pinpoint AI opportunities.
Ontologies are used to classify and organize data, facilitate communication and collaboration, and articulate the constructs and relationships that represent concepts or ideas as domains of understanding. The use of ontologies has historically been grassroot, and frequently appear when professionals across backgrounds and cultures attempt to standardize a subject matter or business domain. However, SmartSystems has observed that the evolution of Web 3.0 is placing the spotlight on the Semantic Web, and among some groups both terms are used interchangeably. This implies that as Web 3.0 metamorphize as a replacement for Web 2.0 so will the Semantic Web, and in turn the use of ontologies to establish common standards will follow.
Knowledge Engineering
Through our history as an AI solutions provider, SmartSystems has implemented Expert Systems to emulate the actions of human subject matter experts in specific domains. A sound example of this is when an engineering expert is confounded with several production options but only has the resources to implement one. The expert, with decades of experience / knowledge of the situation has well defined rules of engagement to select and guide a successful outcome. These rules of engagement may have become standardized and procedural over time and accepted to be reliable and trustworthy. In its attempt to identify candidate AI systems, SmartSystems gravitates towards proven rules based systems that can be codified into AI / ML rules engines.
Knowledge Engineering is concerned with the Acquisition, Representation, Inference, and Management of the accumulated experience of a human expert, where the term accumulated experience connotates acquired knowledge. SmartSystems scans the knowledge portfolio of an organization, paying attention to exceptional skills and unique talent that if computer codified into a rules based AI with ML routines can be an advantage facilitating speed, cost, growth, or the realization of other beneficial metrics. The rules that govern Expert Systems is a Knowledgebase which becomes further enriched as newer experiences are encountered, directly causing the ML routines to automatically codify new heuristics representing the recent encounters.
It is clearly evident that AI is growing at an alarming rate, and the most recent survey puts this market at over $200 by 2025. SmartSystems observes that Knowledge Engineering and tools such as Knowledge Graphs and Knowledgebases will become intertwined with AI. This is especially the cases with Narrow AI, or that class of AI that addresses specific domains of engineering and science through the implementation of Expert Systems. This implies that as AI flourishes, knowledge engineering will follow and will continue to remain a potent subset of AI tools and techniques retrieved upon when the domain in question is narrowly focused and driven by standardized rules that can be easily codified and reinforced with ML.

Request a Quote or Demo
SmartSystems has a diverse portfolio of deployable AI Models. We encourage you to request an AI Application Quotation / Demonstration in a Business Domain of immediate value to you.
